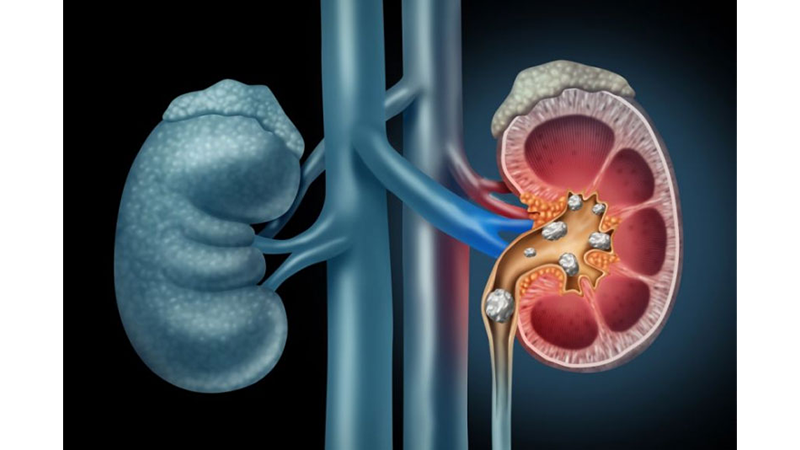
Kidney stone disease is a chronic, recurrent metabolic disease, characterized by the presence of stones in the urinary system, i.e. in the kidneys, urinary tract and bladder.
The main reason for the emergence and development of kidney stone disease is considered a metabolic disorder, which leads to the formation of insoluble salts that form stones. The number of stones and their location can be very different.
Nutritional factors can also cause kidney stone disease. For example, poor and dirty water, monotonous nutrition, climatic characteristics of the region where people live, such as too hot climate, certain medications, abnormal development of the urinary system, hyperparathyroidism, vitamin A and D deficiency, chronic inflammatory diseases of the urinary system (pyelonephritis, cystitis) and hereditary factor.
Depending on the reasons for formation and composition, the stones are divided into several types:
-calcium - up to 70%;
-Uric acid - up to 12%;
-infected - up to 15%;
-cystine stones - up to 2-3%.
Symptoms
Depending on the location of the stone, the patient may exhibit different symptoms. The main symptoms of this disease are:
-Sharp pains. Kidney and upper ureter stone is usually characterized by pain from the back or side right under the ribs. The pain can be acute and blunt, the intensity can vary from 20 to 60 minutes. Often this is preceded by physical activity, taking large amounts of fluid or diuretics. As the stone moves along the ureter, the location of pain changes, the pain goes from the lower back to the abdomen, to the crotch, to the inner thigh, to the scrotum. These manifestations are complemented by frequent calls to urination. It is very important not to confuse renal colic with acute surgical diseases, such as acute appendicitis, acute cholecystitis, acute pancreatitis, intestinal obstruction, pinched hernia, ectopic pregnancies, gastric ulcer, duodenal ulcer. Therefore, in the presence of these symptoms it is extremely important to consult with a doctor as soon as possible to determine the cause of the ailment.
-An admixture of blood in urine. In case of urolithiasis, the appearance of blood in the urine is preceded by renal colic. Blurry urine with sedimentation or smell of stench may also indicate that the stone has escaped.
-Deterioration of general health, in particular nausea, vomiting. These symptoms are especially characteristic of inflammation - pyelonephritis.
-Sand or stone vomiting - When the stone comes out, it may cause chills and fever.
Kidney stone disease examination
In case of the above described complaints it is necessary to consult with an urologist, who, if necessary, will prescribe additional examinations and decide on further treatment.
The basic examination includes:
-collection of anamnesis, examination of the patient;
- general clinical blood and urine analysis;
-Ultrasound of the urinary system.
Additional examinations may include:
- computed tomography.
-seeding of urine with the determination of sensitivity to antibiotics can detect the presence of infection in the urinary tract, the degree of inflammation.
Treatment:
-Medical treatment aimed at independent stone removal;
-medical treatment aimed at dissolving the stone;
-open surgical interventions;
-distant shock-wave lithotripsy;
-endoscopic contact lithotripsy;
-endoscopic surgical interventions.
The question of choosing the method of medical care should be decided by qualified urologists who have modern equipment for diagnosis and treatment of all types of urolithiasis.
Bless you!!!